Difference between revisions of "2N3906 PNP General Purpose Amplifier"
(Created page with "Image:2N3906_data.jpg ==Documents== * File:Fairchild_2N3906.pdf ===Other Packages=== * 2N3906 PNP General Purpose Amplifier * [[MMBT3906|MMBT3906 PNP Gene...") |
m |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Image:2N3906_data.jpg]] | + | [[Image:2N3906_data.jpg|left]] |
| + | |||
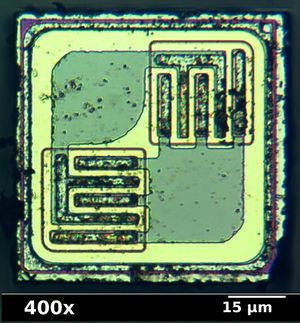
| + | [[Image:2N3906 top metal.jpg|thumb|right|Photomicrograph of the transistor "chip" inside a 2N3906 transistor package, showing the conductive metal layers used to connect the semiconductor junctions to the package leads. The upper-left and lower-right quadrants are [[bonding pad]] areas where wires for two of the terminals will attach, and the other two quadrants have the actual transistor structures, in a bulk region that is contacted at the back side of the chip to the third terminal. ]] | ||
| + | |||
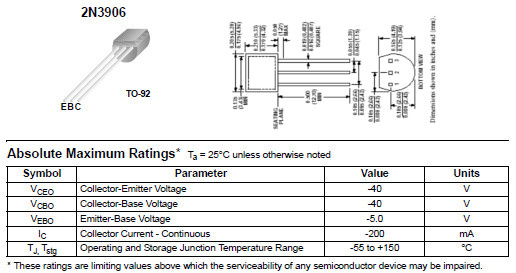
| + | The '''2N3906''' is a common [[PNP transistor|PNP]] [[Bipolar Junction Transistor|bipolar junction transistor]] used for general purpose low-power [[amplifier|amplifying]] or switching applications. Compared to the general run of silicon transistors, it is designed for low [[electric current|current]] and [[electric power|power]] and medium [[voltage]], and can operate at moderately high speeds. The type was registered by Motorola Semiconductor in the mid-sixties, together with the complementary NPN type [[2N3904]]. It has a plastic TO-92 case. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When looking at the flat side with the wires pointed downward, the three wires emerging from the transistor are, left to right, the emitter, base, and collector leads. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is a 200-[[milliamp]], 40-[[volt]], 300-[[milliwatt]] transistor with an [[Transition frequency|F<sub>t</sub>]] of 250 [[MHz]], with a [[Bipolar_junction_transistor#Transistor 'alpha' and 'beta'|beta]] of at least 100.<ref>{{Citation|author-link=Fairchild_Semiconductor|title=Datasheet for Fairchild Semiconductor's typical 2N3906|url=http://www.fairchildsemi.com/ds/2N/2N3906.pdf|date_accessed=2011-05-15}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:2N3906.jpg|thumb|right|Just another little black plastic package - but inside is the the shiny chip seen above. These are stamped with the E,B,C lead identification which makes them kind to students in electronics classes.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{reflist}} | ||
==Documents== | ==Documents== | ||
| Line 5: | Line 19: | ||
===Other Packages=== | ===Other Packages=== | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[2N3906 PNP General Purpose Amplifier|2N3906]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[MMBT3906 PNP General Purpose Amplifier|MMBT3906]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[PZT3906 PNP General Purpose Amplifier|PZT3906]] |
[[Category:Electronic Component (Transistor)]] | [[Category:Electronic Component (Transistor)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:30, 3 March 2013
The 2N3906 is a common PNP bipolar junction transistor used for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. Compared to the general run of silicon transistors, it is designed for low current and power and medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. The type was registered by Motorola Semiconductor in the mid-sixties, together with the complementary NPN type 2N3904. It has a plastic TO-92 case.
When looking at the flat side with the wires pointed downward, the three wires emerging from the transistor are, left to right, the emitter, base, and collector leads.
It is a 200-milliamp, 40-volt, 300-milliwatt transistor with an Ft of 250 MHz, with a beta of at least 100.[1]
References
Cite error: Invalid <references> tag;
parameter "group" is allowed only.
<references />, or <references group="..." />