2N3904 NPN
The 2N3904 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor used for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. The type was registered by Motorola Semiconductor in the mid-sixties, together with the complementary PNP type 2N3906, and represented a significant performance/cost improvement, with the plastic TO-92 case replacing metal cans. It is designed for low current and power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. This transistor is low cost, widely available and sufficiently robust to be of use by experimenters.[1] When looking at the flat side with the base pointed downward, the three wires emerging from the base are, left to right, the emitter, base and collector leads.[2]
It is a 200 mA, 40 volt, 625 milliwatt transistor with a transition frequency of 300 MHz,[3] with a minimum beta or current gain of 100 at a collector current of 10 mA. It is used in a variety of analog amplification and switching applications.
Electrically similar devices are available in a variety of small through-hole and surface mount packages including TO-92, SOT-23, and SOT-223, with package-dependent thermal ratings from 625 milliwatts to 1 watt.
A 2N3906 is a complementary (PNP) transistor for the 2N3904. The 2N2222 is an NPN transistor that can safely switch three times as much current as the 2N3904 but has otherwise similar characteristics.[4] Nevertheless, in many applications such as variable frequency oscillators where lower currents are used to minimize thermal heating and consequent thermal drift of the fundamental frequency, the greater current capacity of the 2N2222 gives it no advantage. Whereas the 2N2222 is optimized to reach its highest gain at currents of around 150 mA, the 2N3904 is optimized for currents of around 10 mA.
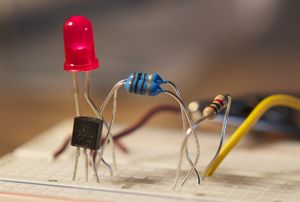
The 2N3904 is used very frequently in hobby electronics circuits including home-made ham radios, code practice oscillators and as an interfacing device for micro-controllers.
References
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedsilver2008 - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedpredko2004 - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedfairchild_sc - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs nameddr_2N2222
Further reading
- Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.